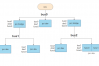
The TLS (Transport Layer Security) handshake process is a cryptographic procedure that occurs when a client initiates a secure communication session with a server.
The TLS handshake involves several steps:
Client Hello: The client sends a message to the server, including supported TLS versions, cipher suites, and random values.
Server Hello: The server responds with its chosen cipher suite, the server’s SSL/TLS certificate, and another random value.
Certificate Request: If required by the server, the server will request a digital certificate from the client, in order to authenticate the client’s identity.
Server Key Exchange: In some cases, the server may send a public key for use in key exchange.
Client Key Exchange: The client creates a new encryption key for the session, encrypts it using the server’s public key, and sends it to the server.
Certificate Verify: If the server requested a certificate from the client, the client must now prove it has the private key associated with the public key provided in the certificate.
Change Cipher Spec: Both the client and server indicate their readiness to begin sending encrypted data.
Finished: Both client and server send a message indicating the completion of the handshake process.
Once the TLS handshake is completed successfully, the client and server can securely exchange data using the agreed-upon encryption parameters.